The engine is powered by the combustion of fuel in the cylinder to generate power. Because the amount of fuel input is limited by the amount of air drawn into the cylinder, the power generated by the engine is also limited, if the engine's operating performance is at its best. Increasing the output power can only increase the amount of fuel by compressing more air into the cylinder, thereby increasing the engine's power.
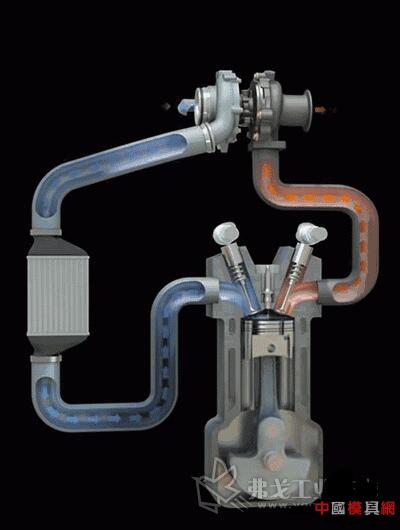
Turbine systems are one of the most common supercharging systems in supercharged engines.
If in the same unit of time, more air and fuel mixture can be forced into the cylinder (combustion chamber) for compression and detonation (small intake engine can be "inhaled" and the same large displacement Air, to increase the volumetric efficiency, can produce greater power output than natural intake engines at the same speed. The situation is like you take an electric fan and blow it into the cylinder. It's hard to pour the wind inside and increase the amount of air inside to get more horsepower. It's just that this fan is not using an electric motor, but using the exhaust gas emitted by the engine. drive.
In general, the engine can increase at least 30% to 40% of the additional power after coordinating such a "forced intake" action. This amazing effect is the reason why the turbocharger is awesome. Moreover, to achieve perfect combustion efficiency and to greatly increase power, the turbocharged system was originally able to provide the greatest value for the vehicle.
What exactly is the working principle of the turbocharger?
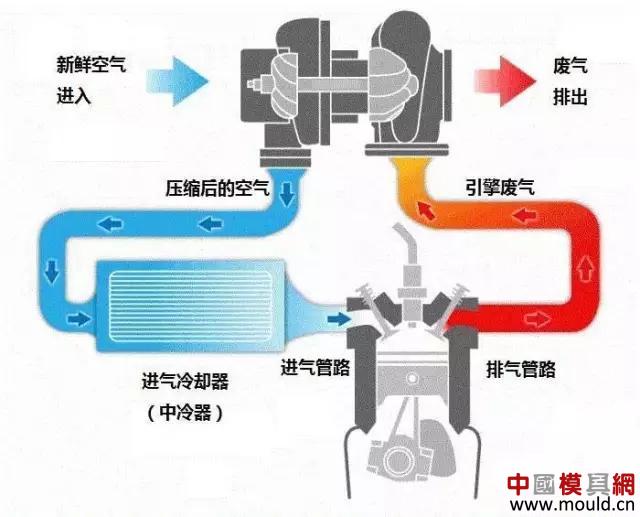
How Turbochargers Work
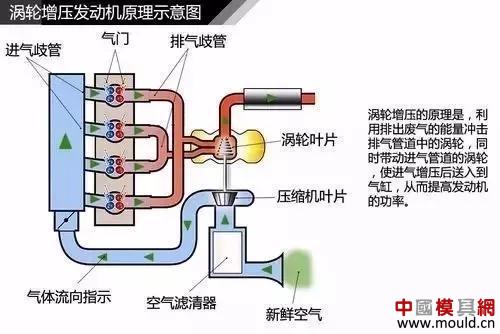
First, the exhaust gas emitted by the engine pushes the turbine wheel at the exhaust end of the turbine (on the right in the figure above) and rotates it. As a result, the compressor wheel (left side) on the other side connected to it can also be rotated simultaneously. The compressor impeller can then induct the air from the air intake, compress it through the rotation of the blades, and then enter the compression channel with smaller and smaller diameter for secondary compression. The compressed air temperature will be higher than that of the direct suction. High, need to be cooled by the intercooler before being injected into the combustion cylinder. This repetition is the working principle of the turbocharger.

The role of throttle
There are two major components in the engine's air intake system. One is the air filter that filters the impurities in the air. The second is the air intake duct that introduces air into the cylinder. In the intake pipe there is a very important part that is the throttle.

Throttle structure
The main role of the throttle is to control the amount of gas mixture entering the cylinder. The depth of the throttle pedal when we drive is actually the size of the throttle opening. The deeper you step on the throttle, the greater the throttle opening, the greater the amount of mixture entering, and the higher the engine speed.
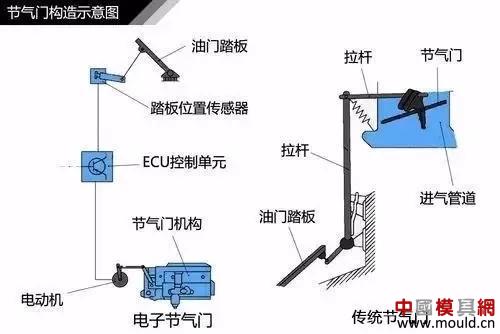
Valve construction diagram
The traditional cable pull throttle is connected to the throttle through one end of the wire and the accelerator pedal. Its transmission ratio is 1:1. This way, the control accuracy is not ideal. Nowadays, the electronic throttle uses a position sensor to transmit data such as the force and amplitude of stepping on the accelerator to the control unit for analysis. The intention of the driver is summed up, and the actual throttle opening degree is calculated by the ECU and a command control section is issued. Valve motor work to achieve precise control of the throttle.
Intake manifold length is variable?
A control valve is installed in the intake manifold. By opening and closing it, the intake manifold can be divided into two sections to change its effective length. Changing the length of the intake manifold is mainly to increase the intake efficiency of the engine at different speeds, and to improve the engine's power performance at various speeds.
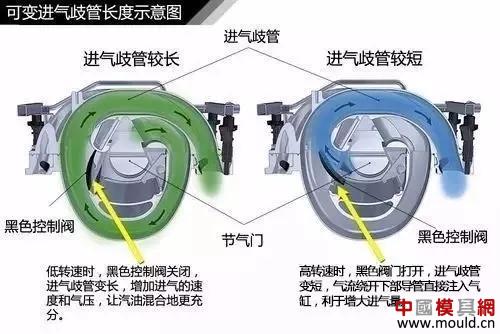
Variable intake manifold schematic
Why is the exhaust manifold "groggy"?
The exhaust system of an automobile mainly includes an exhaust manifold, a three-way catalytic converter, a muffler, and an exhaust pipe. The main role is to exhaust the combustion gases in the cylinder to the atmosphere.
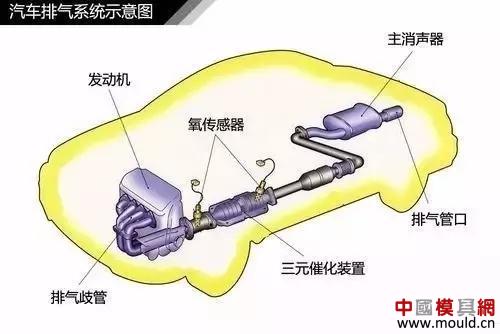
Exhaust system diagram of car
Most of the exhaust pipes we have seen are all oddly shaped. This design is to minimize the mutual interference or exhaust gas recirculation of the exhaust gas emitted by each cylinder and affect the power performance of the engine.

Exhaust manifold schematic
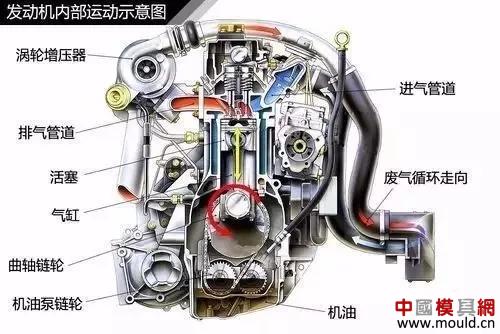
Internal engine schematic
How Turbocharged?
Turbocharger is abbreviated as Turbo or T. Usually we see words such as 1.4T and 2.0T in the rear of the car, indicating that the car's engine is turbocharged.
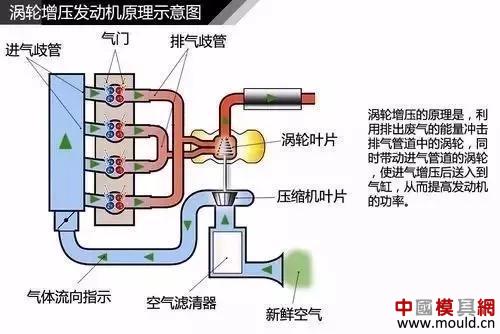
Turbocharged engine principle
The turbocharger is mainly composed of a turbine and a compressor, and is connected via a transmission shaft. The inlet of the turbine is connected to the exhaust manifold of the engine, the outlet of the turbine is connected to the exhaust pipe, the inlet of the compressor is connected to the inlet pipe, and the outlet of the compressor is connected to the inlet manifold. The exhaust gas emitted by the engine impacts the high-speed operation of the turbine, thereby driving the coaxial compressor to rotate at a high speed, forcing the pressurized air into the cylinder.
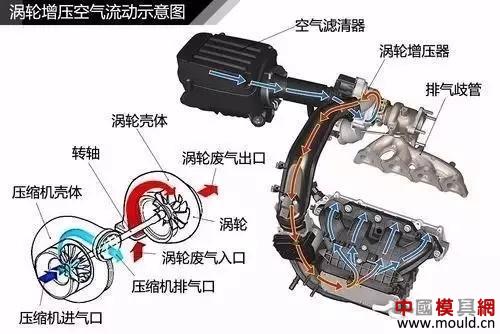
Turbocharged air flow
Turbocharging mainly utilizes the energy of the engine exhaust gas to drive the compressor to achieve the supercharging of the intake air. The engine does not consume the engine power during the entire process, and has good acceleration and sustainability, but the turbine cannot be timely interposed at low speeds. There is a certain lag.
What is the supercharger?
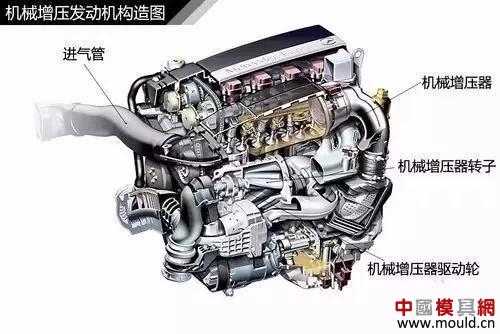
Supercharged engine construction diagram
Supercharger mainly compresses air by driving the rotation of a mechanical air compressor through the power of the crankshaft. However, the power generated by the engine will be lost to a certain extent during the working process.
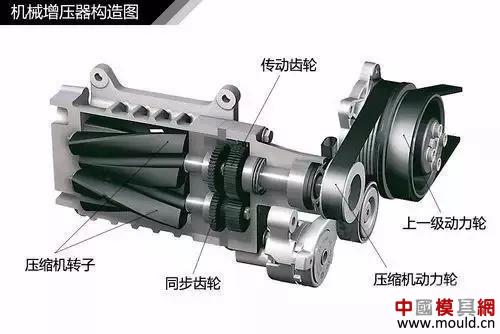
Supercharger construction diagram
Since the supercharger is directly driven by the crankshaft, the supercharger starts to work when the engine is running. Therefore, at low speeds, the engine's torque output performance is also very good, but when the engine is running at high speed, the mechanical turbocharger on the loss of engine power is also very large, the power boost is not obvious.
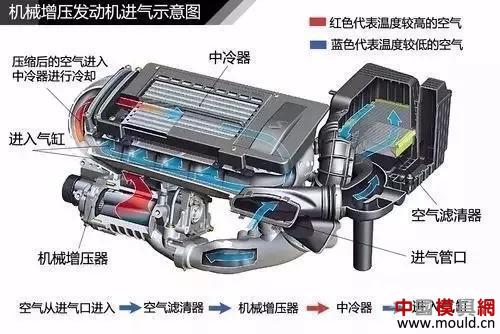
Supercharged engine intake schematic
How does a double booster engine work?
Double booster engine, as the name implies, refers to an engine equipped with two turbochargers. If two turbochargers are used on one engine, it is called a twin turbocharged engine.
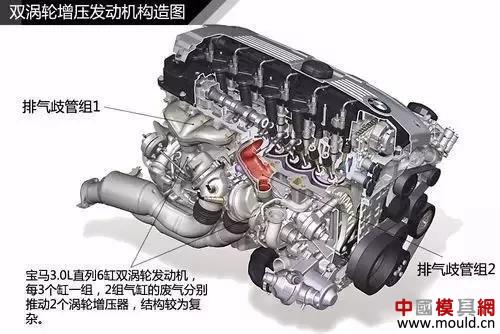
Twin turbocharged engine
For the exhaust gas turbocharged hysteresis, two identical turbines are paralleled on the exhaust pipe. When the engine is running at low speed, less exhaust gas can drive the turbine to rotate at a high speed to generate enough intake pressure to reduce the turbo lag. effect.
As we learned earlier, the turbocharger has hysteresis at low speeds, but at high speeds the boost value is large, the engine power is increased significantly, and the engine power is basically not consumed; and the supercharger is the engine that drives the turbine directly. There is no turbo hysteresis, but the power loss and boost value are low. Once they are combined, they can complement each other.
Double booster engine schematic (turbocharger + supercharger)
With the 1.4-litre TSI engine on the Volkswagen Golf GT, designers combined turbochargers and superchargers. The supercharger is mounted on the engine's air intake system. The turbocharger is mounted on the exhaust system to ensure that the engine has good supercharging effect at low, medium and high speeds.
Steel Doors,Exterior Steel Doors,Metal Door Frame,Steel Security Doors
TAIXING HAITAI GLOBAL TRADE CO.,LTD , https://www.haitship.com